Recent years have seen supply chain challenges grow as an uneven post-pandemic recovery has been met by geopolitical tensions, fresh economic challenges, and a growing climate emergency. While these bottlenecks are likely to stay with us for the foreseeable
future, emerging technologies may provide those affected with some much-needed respite.
So far in 2024, geopolitics and technological advances have become increasingly important topics within supply chain management, and how business is done throughout the industry.
According to the 10th annual Supply Chain Management Priorities and Challenges research paper published at the beginning of the year by APQC,
fewer organizations were able to achieve their business goals in 2023 out of the 350 professionals surveyed globally. But with maturing tech such as generative AI, blockchain, and process automation continuing to present fresh use cases for businesses,
help may be on the way.
Unprecedented Supply Chain Challenges
The state of play for global supply chains was laid bare in early 2024 as attacks and delays in the Suez Canal, coupled with drought caused by the ongoing climate emergency in the Panama Canal, interrupted global shipments for a wide range of businesses.
With maritime transport
accounting for some 80% of the global movement of goods, these issues can risk causing permanent damage to the sustainability of firms alongside their longer-term environmental impact.
In addition to this, geopolitical tensions have caused an increase in tariffs, bans, and various other trade restrictions that can
disrupt the pace of supply chains. With no sign of flare-ups of conflict and intensifying tensions abating, businesses may need to adapt to slowing supply chains quickly.
These pressures make for an unwanted series of additions to a
global supply chain crisis that’s stemmed from severe delays during the COVID-19 pandemic, widespread labor shortages, and a dependence on legacy industry infrastructure.
In the United States, these complications have led to clogged ports and warehouses operating at full capacity.
Finding Solutions in Tech
Despite growing industry bottlenecks, technological innovation is helping to bring more resilience to supplier management and the global trading network in general.
In a tech boom that’s set to herald supply chain 4.0, growing automation and connectivity tools are set to offer a transformative impact on the world of international logistics.
Driving this change will be artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). Recent developments in blockchain have also catapulted the technology to the forefront in the
battle to optimize supply chain management.
These technologies promise to automate logistics management, offer insights in real-time, and streamline essential processes throughout every step of the supply chain.
Furthermore, evidence suggests that businesses have been quick to adopt these innovative new tools. According to
Economist Impact data, 98% of surveyed executives its the Trade in Transition report claimed that they were already using AI tools to streamline at least one aspect of their supply chain
operations.
Digitalization as the Key to Optimization
When it comes to supply chain and vendor management, digitalization holds the key to navigating an increasingly complex industry.
Data from Catena Solutions’ Supply Chain Trends & Insights: Innovation report suggests that organizations nearly doubled their average spending on supply chain innovation in 2023, with
67% of CEOs intent on increasing their investment in disruption detection and innovation processes in the future.
While these processes were once considered a luxury, labor shortages, adverse weather conditions, geopolitics, inflation, and rising consumer demands have made digitalization an essential consideration for all organizations dealing directly with supply chains.
To counter the complicated 2024 landscape, we’re likely to see innovation look to
directly improve supply chain visibility, optimize logistics, and improve adaptability.
There are plenty of emerging use cases that have brought automation into the supply chain management landscape. When it comes to vendor
payouts, the use of real-time AI-driven payments and analytics platforms can help to ensure that all players within a chain are paid on time while discrepancies are quickly identified and addressed.
This means that a payout to specific vendors can be actioned in a fully compliant way, while a bespoke analytics suite means that organizations can keep track of their relationships across every step of the supply chain.
Blockchain in the Supply Chain
Likely, one of the most powerful technologies set to bring greater sustainability to supply chains in the coming years will be
blockchain.
Acting as an immutable ledger, blockchains can help to bring crystal clarity for tracking the origin of goods and building trust throughout the supply chain.
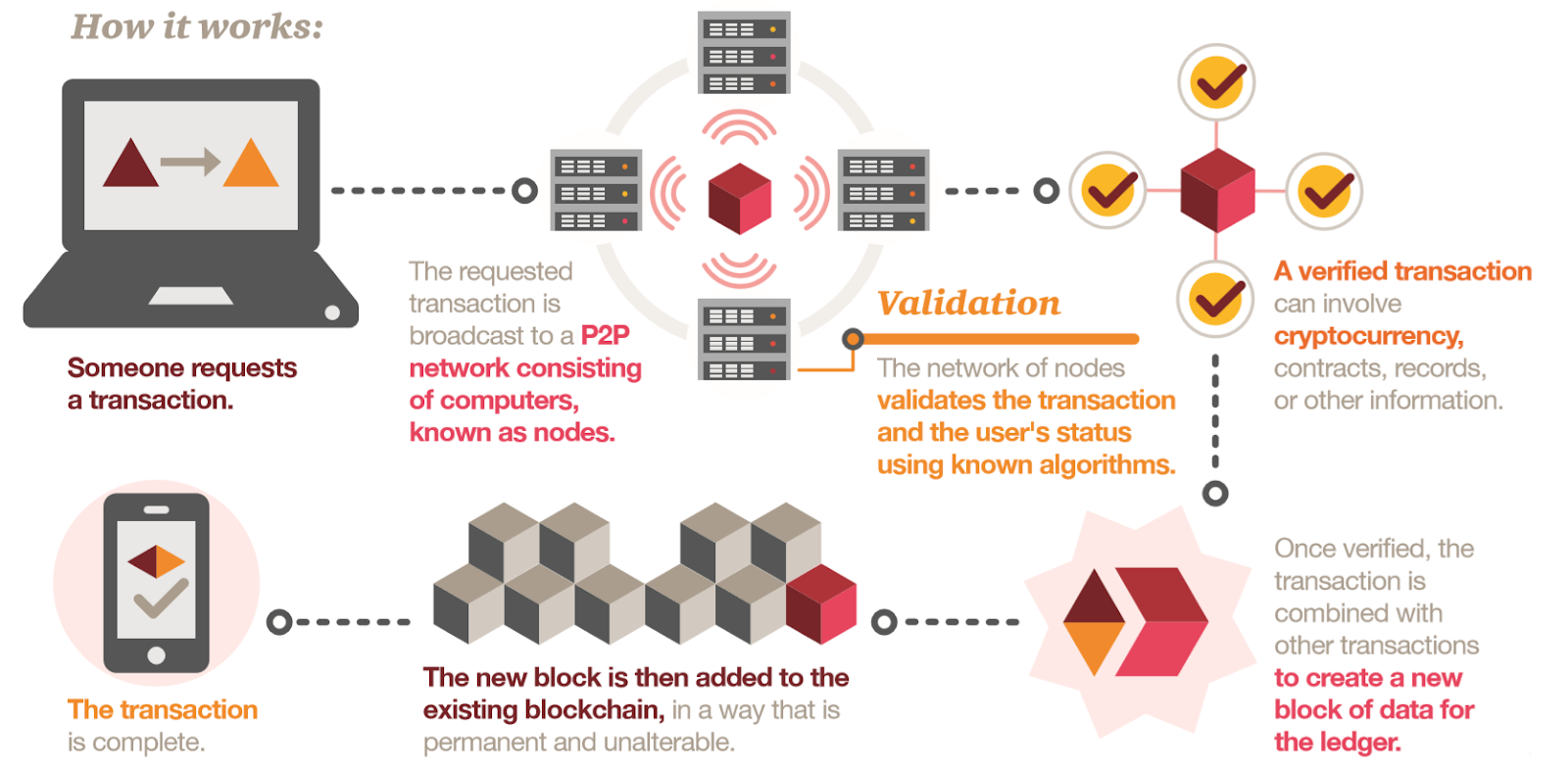
As the diagram above shows, all changes or transactions on the blockchain are subject to network validation, which requires a consensus before a new block is added.
Because all transactions recorded on the blockchain are impossible to tamper with or edit, the technology creates a more holistic audit trail which can
help organizations track vendors in a far more comprehensive manner than through traditional bookkeeping.
Additionally, blockchain technology supports smart contracts, which are automatically designed to execute when a certain series of criteria are met. This means that payments can be linked to quality control teams to ensure that any problems or faulty components
are quickly and accurately identified and resolved before a transaction is made.
In terms of identifying counterfeit goods and instances of fraud in high-risk industries, blockchain can help to bring greater transparency, trust, and security to both organizations and suppliers without having to depend on manual processes to guarantee
quality.
The Growing Role of AI
The ongoing generative AI boom has helped to uncover some of the biggest and most transformative opportunities for supply chain management. Through the technology’s ability to analyze big data and apply algorithmic solutions, AI can offer comprehensive insights
and recommendations for business decision markers.
Actionable insights leveraged by AI will help organizations optimize their supply chain management, bolster resource allocation, and improve efficiency with far greater ease in the near future.
Artificial intelligence is also a
valuable asset in the decision-making process and can help to eliminate human error throughout the landscape. For instance, purchase orders can be automatically generated based on fluctuations in demand, or emerging consumer trends concerning products.
This means that AI can anticipate stock shortages long before they become an issue and make the necessary orders to avoid disruption.
The Age of the Cobot
Robotics will also feature heavily in the evolution of supply chains, and collaborative robots, otherwise known as cobots, will be capable of
assisting human warehouse operatives to optimize time-intensive tasks that can be prone to human error or miscalculations.
Implementing cobots in warehouses throughout supply chains can help to improve task efficiency, accuracy, throughput, and workload management.

Crucially, this additional help at a key stage in the supply chain means that workers won’t be as error-prone in high-pressure, deadline-based working environments. Furthermore, these cobots can work automatically within the Internet of Things (IoT) to record
inventory depletion and even autonomously action fresh orders based on the outflow of goods.
Anticipating New Frontiers in Supply Chain Management
Supply chain digitalization will see many new technologies enter the fray to counter the growing problems facing the industry on a global scale.
Maturing technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and process automation will unite to deliver value on a greater scale for organizations to reap the benefits of more cost and resource-saving processes.
In utilizing these technologies, organizations can continue to leverage stronger levels of trust and efficiency throughout supply chains that may become more complex over time as geopolitics, macroeconomics, and climate change continue to make their presence
felt.